URTICARIA TREATMENT
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition wherein the skin develops red, itching, and raised welts. These welts appear on the skin in varying sizes and shapes and may sometimes combine to make bigger patches. The duration of urticaria depends on its type and can last from minutes up to weeks as Acute Urticaria lasts for less than 6 weeks and Chronic Urticaria: If it exceeds 6 weeks or tends to recur over months/ and or years, then it is classified as chronic.
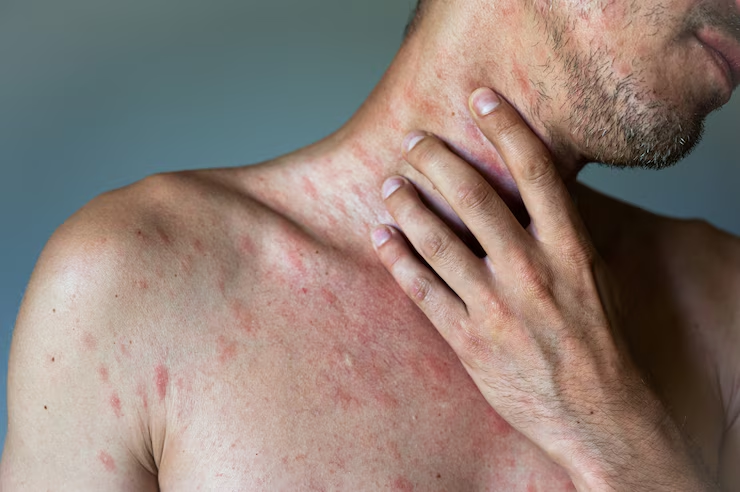
CAUSES OF URTICARIA
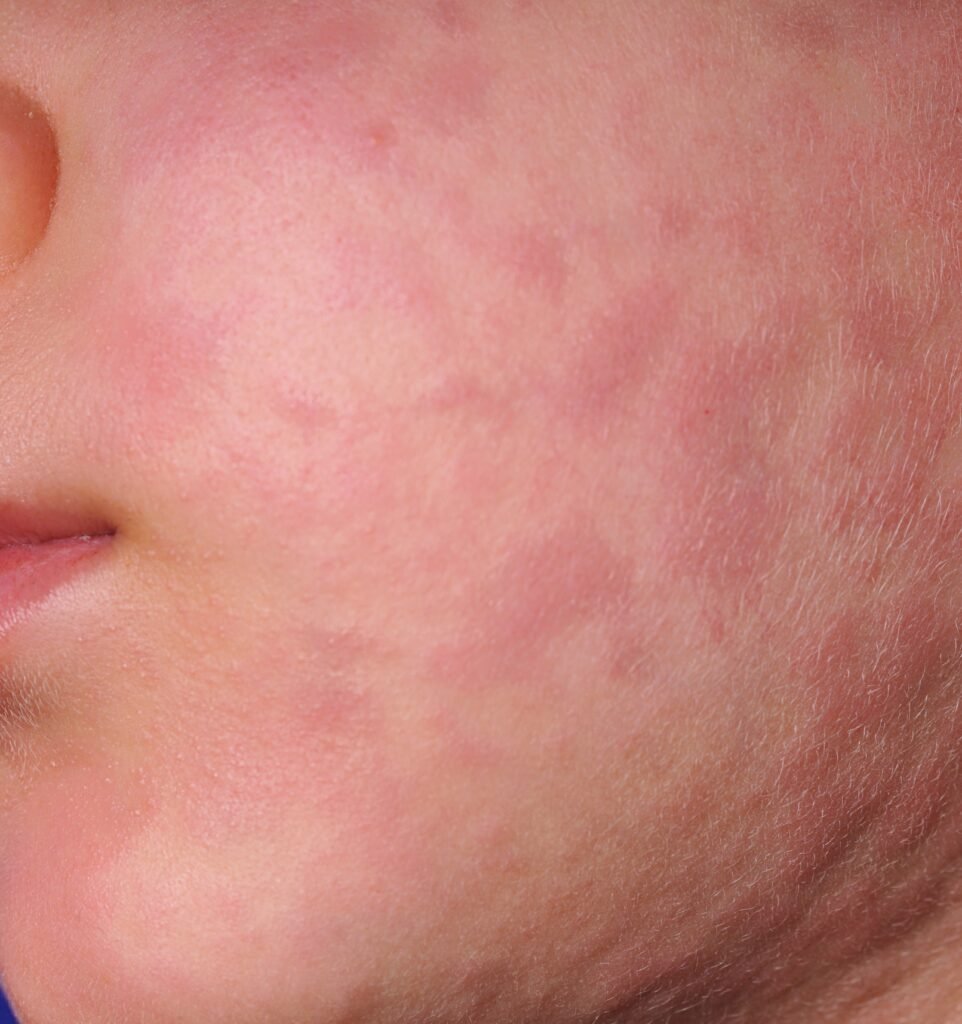
Allergic Reactions
Food allergens (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs, dairy),
Medications (e.g., antibiotics, aspirin, NSAIDs),
Insect bites or stings,
Latex or other materials.
Medications (e.g., antibiotics, aspirin, NSAIDs),
Insect bites or stings,
Latex or other materials.
Non-Allergic Triggers
Infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal infections),
Physical Triggers (heat, cold, or sunlight),
Stress or Emotional Triggers,
Chronic Illness.
Physical Triggers (heat, cold, or sunlight),
Stress or Emotional Triggers,
Chronic Illness.
TREATMENT FOR URTICARIA

Documenting details on triggers, such as common foods, medications, or environments, can be useful to minimize trites.
Do not consume or use known triggers, such as allergens and irritants.
- Apply damp, cold cloths to the areas affected to lessen itchiness and swelling.
- Apply on skin gentle, unscented, and mild moisturizers.
- Clothing: Ensure putting on spacious fitting clothes to avoid any form of discomfort.
- Stress Management: Meditative practices are also effective so that you can use yoga.
- Ongoing treatment with antihistamines or biologics may be necessary.
- An allergist or dermatologist may be required for further evaluation and a comprehensive approach.

