PSORIASIS TREATMENT
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious autoimmune skin disorder that accelerates the life cycle of skin cells, leading to a rapid buildup of cells on the skin’s surface. This buildup forms thick, silvery scales and itchy, dry, red patches that can be painful. Psoriasis can affect different parts of the body, commonly appearing on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back, though it can develop anywhere. The severity of the condition can vary significantly from person to person, ranging from small, localized patches to full-body eruptions.
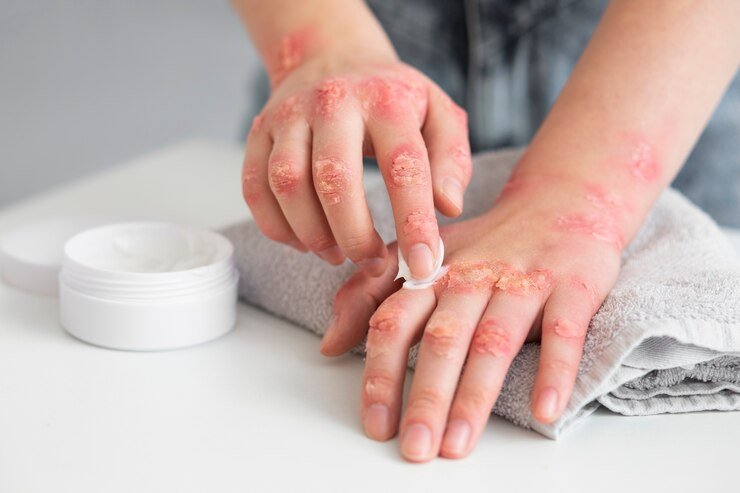

TYPES OF PSORIASIS

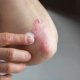
Plaque Psoriasis
It is the most common type and is characterized by raised red scaly patches white to silvery in color on the skin

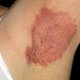
Guttate Psoriasis
Formed due to clogged pores that are filled with oil and skin debris.
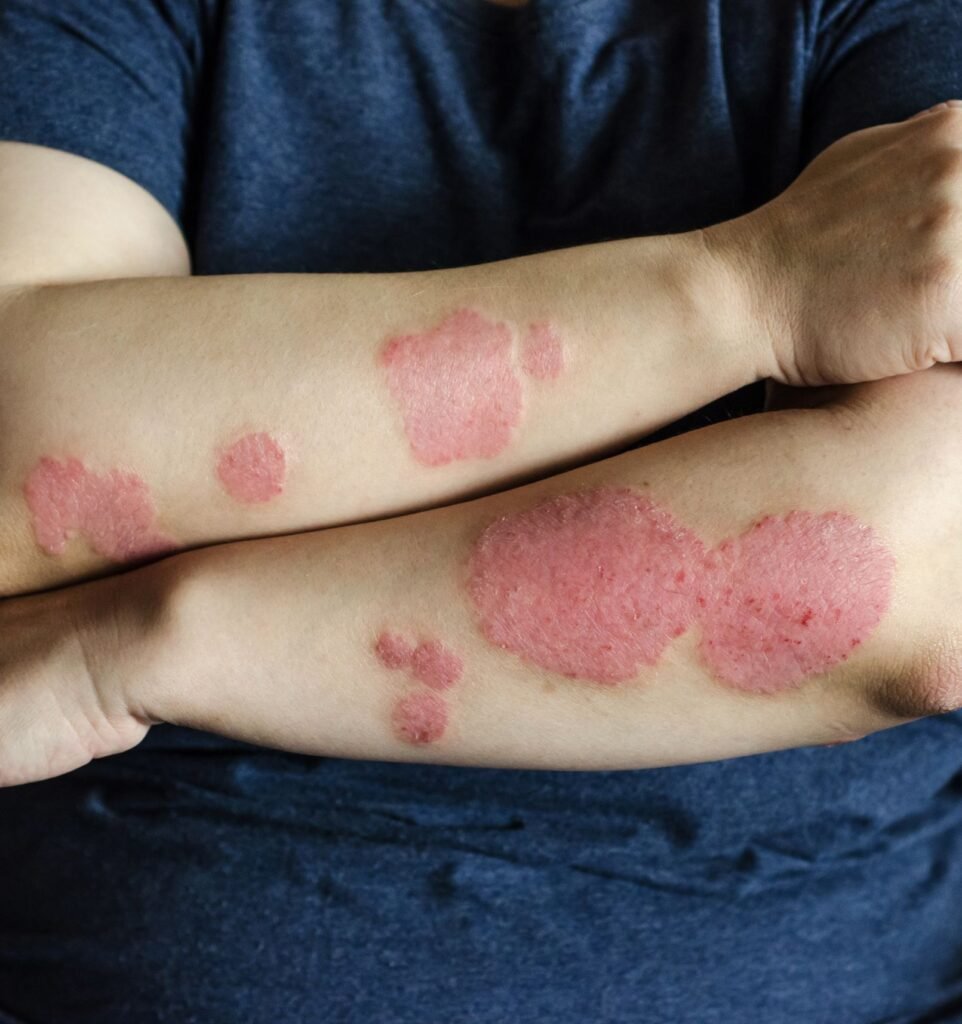
INverse psoriasis
Valid in areas where the skin is touched, skin folds like in between the breasts and in the inner region of the groins.

Pustular psoriasis
This type is characterized by spots and lesions of pus, which occurs at the periphery surrounded by red skin.
CAUSES OF PSORIASIS
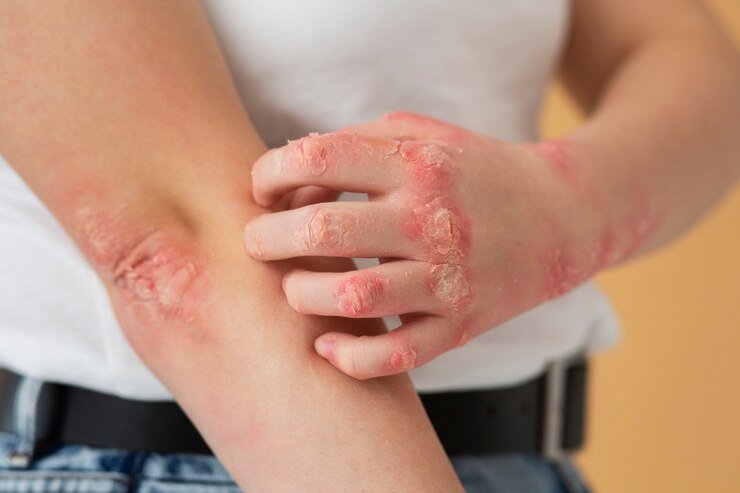
Immune System
Genetics
Triggers
TREATMENT FOR PSORIASIS
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory and reduction in cell production rate.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Calms skin by slowing down excessive growth of cells.
- Coal Tar: Antiscaling, anti-itching and anti-inflammation.
- Salicylic acid: Encourages the shedding of dry skin patches.
- UVB Therapy: Controlled exposure to UV rays decreases the growth rate of skin cells.
- PUVA Therapy: Positively enhances the efficiency of UVA light.
- Biologics: Medications to reduce the effect on immune cells like adalimumab, etanercept, and secukinumab.
- Methotrexate: The drug lowers the function of the immune system, which leads to a reduction in overall inflammation.
- Cyclosporine: Reduces inflammatory response by immune cells; however, there are many side effects.
- Retinoids: These synthetic vitamin A inhibit immature skin cells' growth and make their growth even.
- Moisturizers: The use of emulsions or oils when bathing or showering cuts down dryness.
- Stress Management:
Therapies allow the mind to lose focus on stressors.
Dietary: A diet high in omega-3 and anti-inflammatory foods has been suggested for assistance.
Behaviors To Avoid: See suppression of smoking and excessive alcohol ingestion.

