VITILIGO TREATMENT
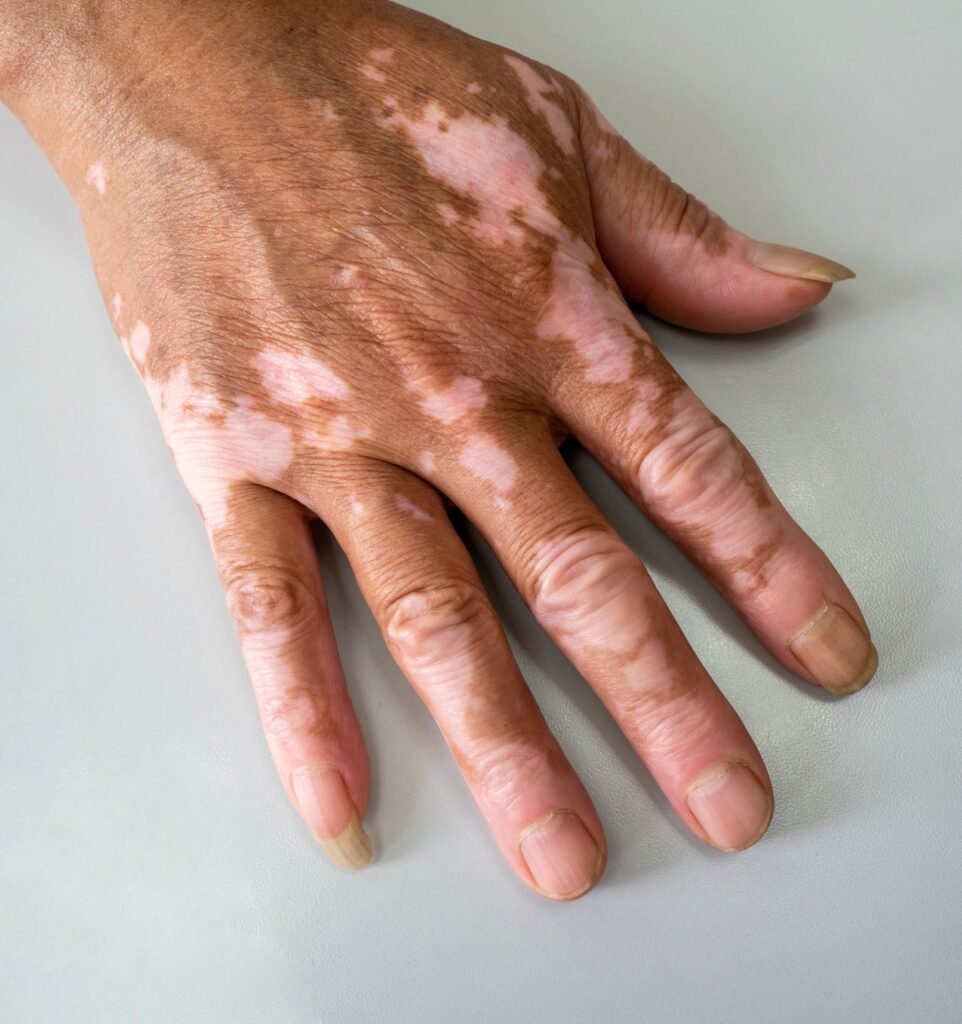
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment in some regions of the skin, resulting in white patches. This occurs because the cells responsible for producing melanin, called melanocytes, are destroyed or stop functioning. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin, hair, and eyes their color, and without it, the affected areas turn white or lighter than the surrounding skin. Vitiligo can affect any part of the body, including the skin, hair, and even the inside of the mouth (mucous membranes).

CAUSES OF VITILIGO
Autoimmune Response
Genetics
Neurogenic Factors
Environmental Triggers
TREATMENT FOR PSORIASIS

Corticosteroids: Useful in treating the early stages of vitiligo, these melanocyte exercising agents are effective in restoring pigmentation with the help of high-potency topical ointment.
Calcineurin Inhibitors (e.g., Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus): Used for treating sensitive areas. Unfortunately, the use of them is quite controversial.
Topical Psoralen: The agent is sparingly useful in boosting the melanin production of unstable melanocytes.
- Skin Grafting: Introduces healthy skin with a normal color to areas where depigmentation is present.
- Blister Grafting: Blisters are formed on pigmented areas and then transferred to areas experiencing loss of pigmentation.
- Micropigmentation (Tattooing): Inserts colour into the skin, which is useful for small zones, like for the lips.
- In cases of widespread vitiligo, it is still possible to even out skin color by depigmenting non-affected skin. This can be done by applying agents, like monobenzone, that inhibit pigmentation in certain areas.
- Counseling or Support Groups: As people develop vitiligo, emotions do take a toll on their lives in terms of self-confidence and anxiety. Counselling assistance, as well as supportive groups, may help in dealing with the situation.
- Sun Protection: V sunscreens formulated for specific needs should be applied on burned areas devoid of melanin.
- Camouflage Products: Depigmented areas can be concealed using makeup or self-tanners available in the market.
- Healthy Diet: Consumption of foods that are high in antioxidants may help in lowering oxygen stress.
- Avoid Skin Trauma: Wounds to the skin or even irritation can elicit the emergence of new patches on the skin (Koebner phenomenon).

